
The Production Development Engineer is responsible for optimizing production processes in the manufacturing environment. It is responsible for creating a collaborative environment that will ensure the delivery of quality products on time. It is important that you are adaptable, innovative, and a good communicator. You must also have strong analytical skills and a development-oriented mentality.
As part of the Advanced Manufacturing Engineering Team the Production Development Engineer works with cross-functional teams. He/she will look for problems in current product and development processes and then use process tech to increase productivity and quality, decrease costs, and reduce cost. The Production Development Engineer will also work with external vendors to resolve technical issues.
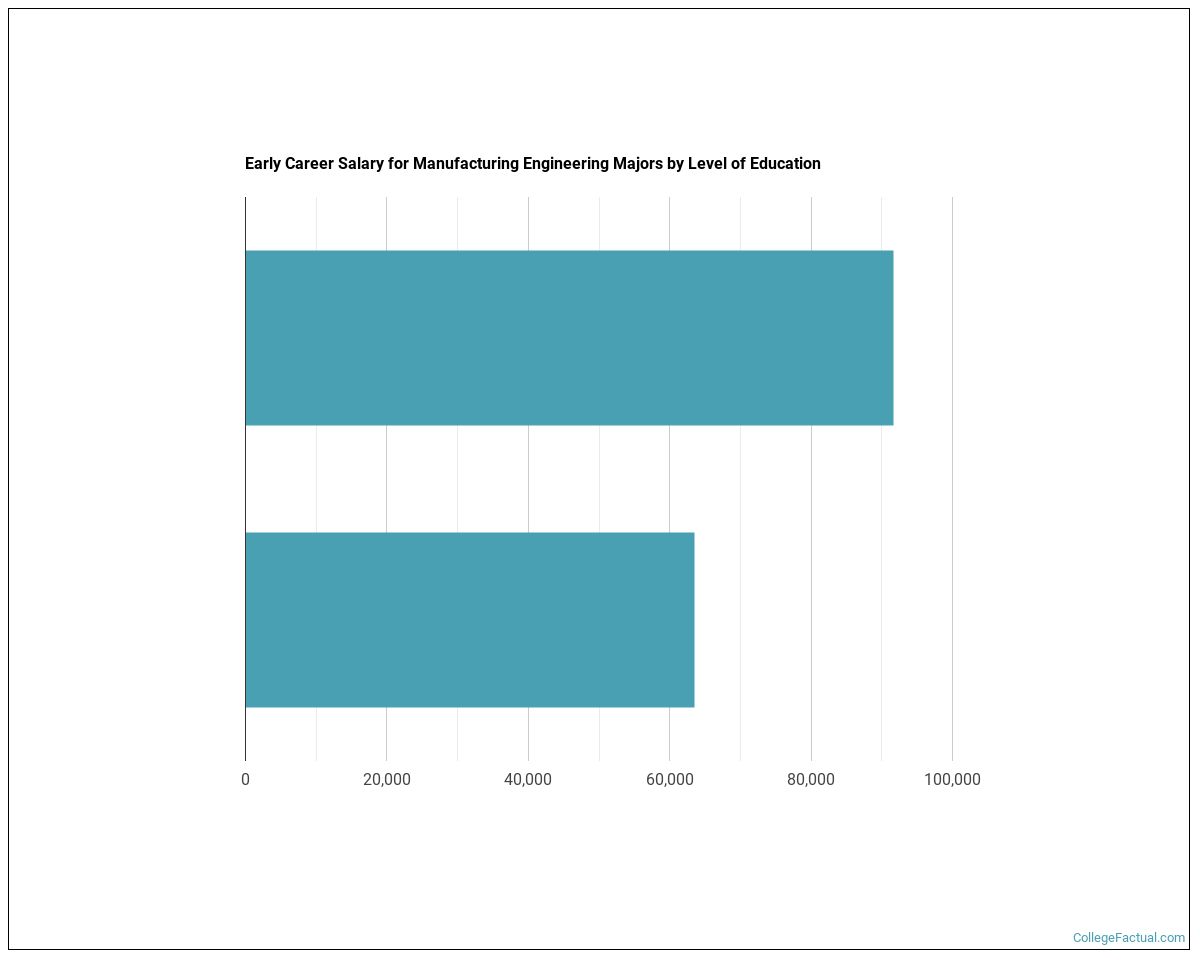
The position requires a bachelor's in engineering and at least three years experience in a manufacturing environment. Strong knowledge of Lean manufacturing is a plus. You will need to be able to communicate technical information and write reports. The Production Development Team can use you if you are passionate about innovation and cost-effective solutions.
They are responsible for developing new product ideas. They are responsible for identifying customer needs and preferences, analysing data and creating product prototypes. They also manage quality control and prepare specifications for production. At the same time, they analyze and test the proposed product to determine any problems or design tolerances. These tasks require strong mathematical and analytical abilities.
A Production Development Engineer with a high level of success will be creative, efficient, and resourceful. In addition to designing new products, he or she must be able to meet budgetary expectations and stakeholder needs. This requires extensive industry experience in product design and an understanding of manufacturing processes.
Product engineers often work in the areas of electrical, materials, or software expertise. Optics, mechanics, testing are all possible areas of expertise. The production development engineer is involved in all stages of a project. He or she will be responsible for ensuring that production methods and equipment are used in order to achieve the product's quality goals, as well as cost and time.
During the product development phase, the Product Development Engineer will review and test the product for potential issues or design tolerances. Next, the Product Development Engineer will design a new prototype using built-in control elements that help to save money during manufacturing.

Once the design is completed, the Product Development Engineer will coordinate activities from the production team and other departments. Then, he or she will develop a quality program to ensure that the product meets all requirements. This includes all safety and environmental issues. The engineer will also deliver approved product designs to the production crew.
The Production Development Engineer must have a good working knowledge of 3D modeling and surface modelling software. A background in the assembly industry is a plus.
FAQ
What kind of jobs are there in logistics?
There are many types of jobs in logistics. Here are some:
-
Warehouse workers – They load and unload pallets and trucks.
-
Transportation drivers - They drive trucks and trailers to deliver goods and carry out pick-ups.
-
Freight handlers are people who sort and pack freight into warehouses.
-
Inventory managers – They manage the inventory in warehouses.
-
Sales representatives: They sell products to customers.
-
Logistics coordinators are responsible for organizing and planning logistics operations.
-
Purchasing agents are those who purchase goods and services for the company.
-
Customer service representatives - Answer calls and email from customers.
-
Shipping clerks - They process shipping orders and issue bills.
-
Order fillers - They fill orders based on what is ordered and shipped.
-
Quality control inspectors (QCI) - They inspect all incoming and departing products for potential defects.
-
Others - There is a variety of other jobs in logistics. These include transportation supervisors and cargo specialists.
What makes a production planner different from a project manger?
The main difference between a production planner and a project manager is that a project manager is usually the person who plans and organizes the entire project, whereas a production planner is mainly involved in the planning stage of the project.
What are the four types of manufacturing?
Manufacturing is the process by which raw materials are transformed into useful products through machines and processes. Manufacturing can include many activities such as designing and building, testing, packaging shipping, selling, servicing, and other related activities.
Statistics
- It's estimated that 10.8% of the U.S. GDP in 2020 was contributed to manufacturing. (investopedia.com)
- (2:04) MTO is a production technique wherein products are customized according to customer specifications, and production only starts after an order is received. (oracle.com)
- According to the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO), China is the top manufacturer worldwide by 2019 output, producing 28.7% of the total global manufacturing output, followed by the United States, Japan, Germany, and India.[52][53] (en.wikipedia.org)
- In the United States, for example, manufacturing makes up 15% of the economic output. (twi-global.com)
- Many factories witnessed a 30% increase in output due to the shift to electric motors. (en.wikipedia.org)
External Links
How To
How to Use Just-In-Time Production
Just-in-time is a way to cut costs and increase efficiency in business processes. It is a process where you get the right amount of resources at the right moment when they are needed. This means that you only pay for what you actually use. The term was first coined by Frederick Taylor, who developed his theory while working as a foreman in the early 1900s. Taylor observed that overtime was paid to workers if they were late in working. He decided to ensure workers have enough time to do their jobs before starting work to improve productivity.
The idea behind JIT is that you should plan ahead and have everything ready so you don't waste money. Look at your entire project, from start to end. Make sure you have enough resources in place to deal with any unexpected problems. You can anticipate problems and have enough equipment and people available to fix them. This way you won't be spending more on things that aren’t really needed.
There are several types of JIT techniques:
-
Demand-driven JIT: This is a JIT that allows you to regularly order the parts/materials necessary for your project. This will enable you to keep track of how much material is left after you use it. This will allow to you estimate the time it will take for more to be produced.
-
Inventory-based: This type allows you to stock the materials needed for your projects ahead of time. This allows you to predict how much you can expect to sell.
-
Project-driven: This is an approach where you set aside enough funds to cover the cost of your project. Knowing how much money you have available will help you purchase the correct amount of materials.
-
Resource-based JIT : This is probably the most popular type of JIT. Here, you allocate certain resources based on demand. If you have many orders, you will assign more people to manage them. If there aren't many orders, you will assign fewer people.
-
Cost-based : This is similar in concept to resource-based. But here, you aren't concerned about how many people your company has but how much each individual costs.
-
Price-based pricing: This is similar in concept to cost-based but instead you look at how much each worker costs, it looks at the overall company's price.
-
Material-based - This is a variant of cost-based. But instead of looking at the total company cost, you focus on how much raw material you spend per year.
-
Time-based JIT is another form of resource-based JIT. Instead of focusing on how much each employee costs, you focus on how long it takes to complete the project.
-
Quality-based JIT: Another variation on resource-based JIT. Instead of thinking about how much each employee costs or how long it takes to manufacture something, you think about how good the quality of your product is.
-
Value-based: This is one of the newest forms of JIT. In this case, you're not concerned with how well the products perform or whether they meet customer expectations. Instead, your focus is on the value you bring to the market.
-
Stock-based is an inventory-based system that measures the number of items produced at any given moment. This method is useful when you want to increase production while decreasing inventory.
-
Just-intime planning (JIT), is a combination JIT/sales chain management. This refers to the scheduling of the delivery of components as soon after they are ordered. This is important as it reduces lead time and increases throughput.