You will need to have the right education and training to be a manufacturing engineer. A master's degree program is available for some graduates that focuses on product, business and process knowledge. The majority of manufacturing engineers obtain the bulk of their training during their degree program. They have hands-on experience in standard and experimental testing, measurement, and experimentation. To be allowed to do business, they must have a license. This shows employers that the candidate is qualified.
Manufacturing engineers need to have the following skills
Manufacturing engineers can rise from an entry-level to a managerial position depending on their position. They will be required to have the following skills in order to succeed: They should have knowledge in a variety of disciplines, including math and critical thought. A manufacturing engineer should be able to communicate effectively with people at all levels of the organization. These are just a few of the many skills that a manufacturing engineer will need to be successful in their role.
Manufacturing engineers are responsible for the design, maintenance and modification of different processes and systems. They will also be responsible for the environmental impact of manufacturing processes. They need to be creative thinkers, designers and have a good understanding of manufacturing processes. Manufacturing engineers need to keep up with the latest trends and regulations as well as industry news. Furthermore, they should be able to work with other engineers in different fields.

Manufacturing engineer responsibilities
A manufacturing engineer's responsibilities include developing production processes and determining production cost. A manufacturing engineer is responsible for developing and designing production processes. They also troubleshoot and analyze manufacturing processes and materials. While most of their work is done in the office, they might be required to travel to other locations (e.g. to the factory floor). Some manufacturing engineers may be required to supervise production personnel or direct technicians. They are responsible for the smooth operation of a production line.
A manufacturing engineer's main task is to plan and implement manufacturing processes. They also monitor their effectiveness. Manufacturing engineers are responsible for analyzing production processes and designing equipment. They also create quality control systems to ensure that products meet the highest quality standards. Apart from designing and developing manufacturing process, they must also comply with safety and regulatory standards. A manufacturing engineer's duties extend beyond their workplace. They must also conduct research and create reports and documentation.
For manufacturing engineers, the future looks bright
Manufacturing engineers are a highly skilled occupation with a bright future. Although their growth is slower than that of other occupations, job creation is expected higher than average. The growth of the manufacturing sector will contribute to the employment of manufacturing engineers. Manufacturing companies are dependent on the ability to plan and implement logistics. Despite slow growth there is a high demand for mechanical engineering. Most job seekers will start in the school system.
According to Bureau of Labor Statistics, the U.S.'s number of manufacturing professionals is expected increase by 9% from 2026. These professionals need to enjoy teamwork and a challenging job environment. Manufacturing engineers enjoy high levels of job satisfaction and are often able to stay in the field for many years. For example, manufacturing engineers may work in a factory that produces cars or trucks. Manufacturing engineers may also be employed in consulting services, research and development firms, or wholesale trade. Some industrial engineers move into managerial roles after leaving engineering.
For manufacturing engineers, education requirements
For most manufacturing jobs, an undergraduate degree in engineering (BSE), will be required. Students can expect to learn about general science and math as well as engineering concepts. Students can expect to learn communication skills, as well as a solid foundation of mathematics. Courses in humanities or ethics may also be required. There are many education requirements for manufacturing engineering engineers, but they can be varied, but BSEs are generally well-rounded.
Manufacturing engineering requires strong math and science background, along with analytical and problem-solving skills. As well as being creative, they need to be able to work in a team. Manufacturing engineers typically work full-time after graduation. Their job requires them to travel, observe manufacturing operations in different places and perform other duties. Manufacturing engineers need to have strong work ethics and a passion for learning about new trends in manufacturing.
FAQ
How does a production planner differ from a project manager?
The main difference between a production planner and a project manager is that a project manager is usually the person who plans and organizes the entire project, whereas a production planner is mainly involved in the planning stage of the project.
What does the term manufacturing industries mean?
Manufacturing Industries are those businesses that make products for sale. Consumers are people who purchase these goods. These companies employ many processes to achieve this purpose, such as production and distribution, retailing, management and so on. They create goods from raw materials, using machines and various other equipment. This includes all types manufactured goods such as clothing, building materials, furniture, electronics, tools and machinery.
Can some manufacturing processes be automated?
Yes! Since ancient times, automation has been in existence. The Egyptians discovered the wheel thousands and years ago. Robots are now used to assist us in assembly lines.
Robotics is used in many manufacturing processes today. They include:
-
Robots for assembly line
-
Robot welding
-
Robot painting
-
Robotics inspection
-
Robots that create products
Manufacturing can also be automated in many other ways. 3D printing makes it possible to produce custom products in a matter of days or weeks.
What are the 7 Rs of logistics.
The acronym 7R's of Logistic is an acronym that stands for seven fundamental principles of logistics management. It was developed by the International Association of Business Logisticians (IABL) and published in 2004 as part of its "Seven Principles of Logistics Management" series.
The acronym is made up of the following letters:
-
Responsible – ensure that all actions are legal and don't cause harm to anyone else.
-
Reliable - have confidence in the ability to deliver on commitments made.
-
Reasonable - make sure you use your resources well and don't waste them.
-
Realistic - consider all aspects of operations, including cost-effectiveness and environmental impact.
-
Respectful: Treat others with fairness and equity
-
Resourceful - look for opportunities to save money and increase productivity.
-
Recognizable provides value-added products and services to customers
How can manufacturing excess production be decreased?
Better inventory management is key to reducing excess production. This would decrease the time that is spent on inefficient activities like purchasing, storing, or maintaining excess stock. By doing this, we could free up resources for other productive tasks.
One way to do this is to adopt a Kanban system. A Kanban board is a visual display used to track work in progress. In a Kanban system, work items move through a sequence of states until they reach their final destination. Each state represents a different priority.
If work is moving from one stage to the other, then the current task can be completed and moved on to the next. But if a task remains in the beginning stages it will stay that way until it reaches its end.
This allows for work to continue moving forward, while also ensuring that there is no work left behind. Managers can view the Kanban board to see how much work they have done. This allows them to adjust their workflows based on real-time information.
Lean manufacturing is another way to manage inventory levels. Lean manufacturing focuses on eliminating waste throughout the entire production chain. Anything that does not contribute to the product's value is considered waste. Here are some examples of common types.
-
Overproduction
-
Inventory
-
Unnecessary packaging
-
Material surplus
These ideas can help manufacturers improve efficiency and reduce costs.
What is production plan?
Production Planning is the creation of a plan to cover all aspects, such as scheduling, budgeting. Location, crew, equipment, props and other details. This document is designed to make sure everything is ready for when you're ready to shoot. It should also provide information about how best to produce the best results while on set. This includes location information, crew details, equipment specifications, and casting lists.
First, you need to plan what you want to film. You might have an idea of where you want to film, or you may have specific locations or sets in mind. Once you have identified your locations and scenes it's time to begin figuring out what elements you will need for each one. One example is if you are unsure of the exact model you want but decide that you require a car. To narrow your options, you can search online for available models.
Once you have found the right vehicle, you can think about adding accessories. You might need to have people in the front seats. Or maybe you just need someone to push the car around. Maybe you'd like to change the interior from black to a white color. These questions will help you determine the exact look and feel of your car. You can also think about the type of shots you want to get. What type of shots will you choose? Maybe you want to show the engine and the steering wheel. All of these things will help you identify the exact style of car you want to film.
Once you have made all the necessary decisions, you can start to create a schedule. You will know when you should start and when you should finish shooting. The schedule will show you when to get there, what time to leave, and when to return home. Everyone will know what they need and when. If you need to hire extra staff, you can make sure you book them in advance. You don't want to hire someone who won't show up because he didn't know.
Also, consider how many days you will be filming your schedule. Some projects only take one or two days, while others may last weeks. When creating your schedule, be aware of whether you need more shots per day. Multiple takes at the same place will result in higher costs and longer completion times. If you are unsure if you need multiple takes, it is better to err on the side of caution and shoot fewer takes rather than risk wasting money.
Budget setting is an important part of production planning. A realistic budget will help you work within your means. If you have to reduce your budget due to unexpected circumstances, you can always lower it later. But, don't underestimate how much money you'll spend. If you underestimate the cost of something, you will have less money left after paying for other items.
Production planning is a detailed process. But, once you understand the workings of everything, it becomes easier for future projects to be planned.
What does warehouse refer to?
A warehouse or storage facility is where goods are stored before they are sold. It can be an indoor space or an outdoor area. It could be one or both.
Statistics
- It's estimated that 10.8% of the U.S. GDP in 2020 was contributed to manufacturing. (investopedia.com)
- Many factories witnessed a 30% increase in output due to the shift to electric motors. (en.wikipedia.org)
- According to the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO), China is the top manufacturer worldwide by 2019 output, producing 28.7% of the total global manufacturing output, followed by the United States, Japan, Germany, and India.[52][53] (en.wikipedia.org)
- In 2021, an estimated 12.1 million Americans work in the manufacturing sector.6 (investopedia.com)
- [54][55] These are the top 50 countries by the total value of manufacturing output in US dollars for its noted year according to World Bank.[56] (en.wikipedia.org)
External Links
How To
How to use lean manufacturing in the production of goods
Lean manufacturing is an approach to management that aims for efficiency and waste reduction. It was created in Japan by Taiichi Ohno during the 1970s and 80s. He received the Toyota Production System award (TPS), from Kanji Toyoda, founder of TPS. Michael L. Watkins published the "The Machine That Changed the World", the first book about lean manufacturing. It was published in 1990.
Lean manufacturing refers to a set of principles that improve the quality, speed and costs of products and services. It emphasizes reducing defects and eliminating waste throughout the value chain. The five-steps of Lean Manufacturing are just-in time (JIT), zero defect and total productive maintenance (TPM), as well as 5S. Lean manufacturing seeks to eliminate non-value added activities, such as inspection, work, waiting, and rework.
Lean manufacturing improves product quality and costs. It also helps companies reach their goals quicker and decreases employee turnover. Lean Manufacturing is one of the most efficient ways to manage the entire value chains, including suppliers and customers as well distributors and retailers. Many industries worldwide use lean manufacturing. Toyota's philosophy has been a key driver of success in many industries, including automobiles and electronics.
Five fundamental principles underlie lean manufacturing.
-
Define Value - Determine the value that your business brings to society. Also, identify what sets you apart from your competitors.
-
Reduce waste - Get rid of any activity that does not add value to the supply chain.
-
Create Flow: Ensure that the work process flows without interruptions.
-
Standardize & Simplify - Make processes as consistent and repeatable as possible.
-
Build Relationships - Establish personal relationships with both internal and external stakeholders.
Although lean manufacturing isn't a new concept in business, it has gained popularity due to renewed interest in the economy after the 2008 global financial crisis. Many companies have adopted lean manufacturing methods to increase their marketability. Many economists believe lean manufacturing will play a major role in economic recovery.
Lean manufacturing has many benefits in the automotive sector. These benefits include increased customer satisfaction, reduced inventory levels and lower operating costs.
It can be applied to any aspect of an organisation. It is especially useful for the production aspect of an organization, as it ensures that every step in the value chain is efficient and effective.
There are three types principally of lean manufacturing:
-
Just-in-Time Manufacturing: Also known as "pull systems", this type of lean manufacturing uses just-in-time manufacturing (JIT). JIT is a method in which components are assembled right at the moment of use, rather than being manufactured ahead of time. This approach is designed to reduce lead times and increase the availability of components. It also reduces inventory.
-
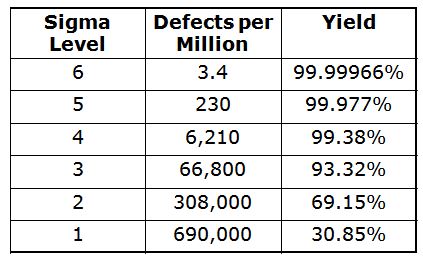
Zero Defects Manufacturing (ZDM),: ZDM is a system that ensures no defective units are left the manufacturing facility. It is better to repair a part than have it removed from the production line if it needs to be fixed. This applies to finished goods that may require minor repairs before shipment.
-
Continuous Improvement (CI), also known as Continuous Improvement, aims at improving the efficiency of operations through continuous identification and improvement to minimize or eliminate waste. Continuous improvement refers to continuous improvement of processes as well people and tools.