Whether it's a product, process or part of the production process, advanced manufacturing can be used in a number of ways to increase productivity and reduce costs. This allows manufacturers to quickly create prototypes and adjust production lines in order to meet design changes. It allows manufacturers to adjust production lines according to customer demand. It can even level the playing fields between large and small producers.
The definition of advanced manufacturing will vary from company to company. It depends on the industry involved, the process used and the purpose of the advanced manufacturing. Advanced manufacturing can include all phases of research, development, design, production, and after-sales services. It can also include the use of innovative technologies. Advanced manufacturing offers the greatest benefits in terms of increased quality and lower production costs. This is achieved by implementing new technologies, such as 3-D printing. Because they are inexpensive, these technologies can be used in a wide variety of industries. This type of manufacturing is also flexible and allows manufacturers to produce customized products in small batches. Advanced manufacturing also allows for a faster time to market.
Manufacturing is one the most important sources of global growth. This sector has a significant economic impact and can create ripple effects that could be felt worldwide. Companies must ensure efficiency in every aspect of their business. This includes rapid piloting of innovative technologies. The manufacturing sector is constantly changing and manufacturers must be ready to respond.
Safety, quality, accuracy, and precision are all important in the manufacturing industry. The goal of advanced manufacturing is to create high-quality products at an affordable price. Besides the use of innovative technologies, it also uses creative methods of production. It is important to create a lean and efficient production line. Advanced manufacturing is characterized by high-tech production systems and information communication technologies.
The manufacturing industry is always in sync with technological advances, including electronic information, materials, and computer technology. Nanotechnology has, for example made advanced manufacturing systems more flexible, less intrusive, and increased the functionality in production lines. It has also helped to decrease the size of devices and minimize the footprint. Automation is also included, which allows workers and managers to concentrate on strategic tasks rather than mundane work. You can also reduce costs and improve the production efficiency of network communications.
The Office of Counterterrorism and Emerging Threats has launched a new section on its website to provide information about advanced manufacturing. The website will continue to provide news, funding opportunities and information. OCET also works with NIST, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), to develop monoclonal antibodies that are thermally stable.
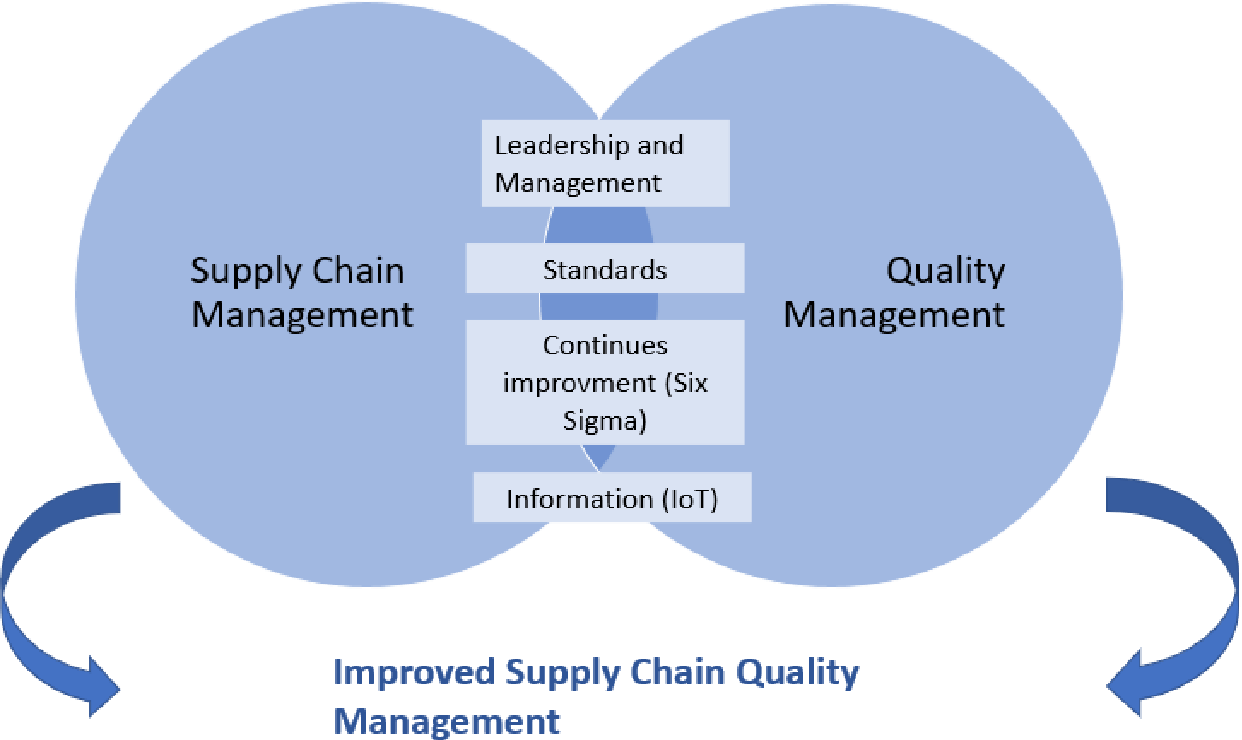
As the manufacturing industry continues to develop, it is becoming more dependent upon information communication technology. This technology allows manufacturers and other machines to communicate with each other, and gives them real-time alerts when there are problems. This technology allows manufacturers to perform precision tuning and provide feedback from the factory floor. This will enable manufacturers to improve their production efficiency and lower maintenance costs.
FAQ
What does it mean to be a manufacturer?
Manufacturing Industries are companies that manufacture products. These products are sold to consumers. To accomplish this goal, these companies employ a range of processes including distribution, sales, management, and production. They produce goods from raw materials by using machines and other machinery. This includes all types manufactured goods such as clothing, building materials, furniture, electronics, tools and machinery.
What is the difference between Production Planning, Scheduling and Production Planning?
Production Planning (PP) refers to the process of determining how much production is needed at any given moment. Forecasting demand is one way to do this.
Scheduling is the process that assigns dates to tasks so they can get completed within a given timeframe.
What is the job of a production plan?
A production planner makes sure all project elements are delivered on schedule, within budget, as well as within the agreed scope. They ensure that the product or service is of high quality and meets client requirements.
Why is logistics important in manufacturing
Logistics are an integral part any business. They help you achieve great results by helping you manage all aspects of product flow, from raw materials to finished goods.
Logistics play an important role in reducing costs as well as increasing efficiency.
How can manufacturing excess production be decreased?
It is essential to find better ways to manage inventory to reduce overproduction. This would decrease the time that is spent on inefficient activities like purchasing, storing, or maintaining excess stock. We could use these resources to do other productive tasks.
You can do this by adopting a Kanban method. A Kanban board is a visual display used to track work in progress. In a Kanban system, work items move through a sequence of states until they reach their final destination. Each state has a different priority level.
For instance, when work moves from one stage to another, the current task is complete enough to be moved to the next stage. It is possible to keep a task in the beginning stages until it gets to the end.
This keeps work moving and ensures no work is lost. Managers can view the Kanban board to see how much work they have done. This information allows managers to adjust their workflow based off real-time data.
Lean manufacturing is another way to manage inventory levels. Lean manufacturing seeks to eliminate waste from every step of the production cycle. Any product that isn't adding value can be considered waste. The following are examples of common waste types:
-
Overproduction
-
Inventory
-
Unnecessary packaging
-
Material surplus
These ideas will help manufacturers increase efficiency and lower costs.
Statistics
- (2:04) MTO is a production technique wherein products are customized according to customer specifications, and production only starts after an order is received. (oracle.com)
- It's estimated that 10.8% of the U.S. GDP in 2020 was contributed to manufacturing. (investopedia.com)
- According to a Statista study, U.S. businesses spent $1.63 trillion on logistics in 2019, moving goods from origin to end user through various supply chain network segments. (netsuite.com)
- [54][55] These are the top 50 countries by the total value of manufacturing output in US dollars for its noted year according to World Bank.[56] (en.wikipedia.org)
- In the United States, for example, manufacturing makes up 15% of the economic output. (twi-global.com)
External Links
How To
How to use the Just-In Time Method in Production
Just-in-time (JIT) is a method that is used to reduce costs and maximize efficiency in business processes. It's the process of obtaining the right amount and timing of resources when you need them. This means you only pay what you use. The term was first coined by Frederick Taylor, who developed his theory while working as a foreman in the early 1900s. He saw how overtime was paid to workers for work that was delayed. He then concluded that if he could ensure that workers had enough time to do their job before starting to work, this would improve productivity.
The idea behind JIT is that you should plan ahead and have everything ready so you don't waste money. Look at your entire project, from start to end. Make sure you have enough resources in place to deal with any unexpected problems. If you expect problems to arise, you will be able to provide the necessary equipment and personnel to address them. This will prevent you from spending extra money on unnecessary things.
There are different types of JIT methods:
-
Demand-driven: This is a type of JIT where you order the parts/materials needed for your project regularly. This will let you track the amount of material left over after you've used it. This will let you know how long it will be to produce more.
-
Inventory-based: You stock materials in advance to make your projects easier. This allows you to predict how much you can expect to sell.
-
Project-driven: This is an approach where you set aside enough funds to cover the cost of your project. Once you have an idea of how much material you will need, you can purchase the necessary materials.
-
Resource-based JIT : This is probably the most popular type of JIT. This is where you assign resources based upon demand. You will, for example, assign more staff to deal with large orders. If you don't have many orders, you'll assign fewer people to handle the workload.
-
Cost-based: This approach is very similar to resource-based. However, you don't just care about the number of people you have; you also need to consider how much each person will cost.
-
Price-based: This approach is very similar to the cost-based method except that you don't look at individual workers costs but the total cost of the company.
-
Material-based: This approach is similar to cost-based. However, instead of looking at the total cost for the company, you look at how much you spend on average on raw materials.
-
Time-based JIT: A variation on resource-based JIT. Instead of worrying about how much each worker costs, you can focus on how long the project takes.
-
Quality-based: This is yet another variation of resource-based JIT. Instead of worrying about the costs of each employee or how long it takes for something to be made, you should think about how quality your product is.
-
Value-based JIT is the newest form of JIT. In this instance, you are not concerned about the product's performance or meeting customer expectations. Instead, you're focused on how much value you add to the market.
-
Stock-based: This stock-based method focuses on the actual quantity of products being made at any given time. This is used to increase production and minimize inventory.
-
Just-in time (JIT), planning: This is a combination JIT/supply chain management. This refers to the scheduling of the delivery of components as soon after they are ordered. It's important as it reduces leadtimes and increases throughput.