
The food manufacturing sector is large and requires many managers and professionals. Top executives are responsible for making policy decisions and organizing production operations. Managers of industrial production oversee the day to day operations at a manufacturing plant. Marketing, public relations and sales managers oversee marketing, promotional and sales programs.
Food manufacturing jobs
The state of New York is home to many food manufacturing jobs. Bakers, food batchmakers, packaging and filling machine operator are the top three most common occupations. These occupations comprise just over half of state's food production employment. Food manufacturing employment increased across the state in seven out 10 labor markets.
A rising number of food manufacturing jobs is correlated with a improving job market. In February, there was a 3.8% unemployment rate, the lowest point in more than ten years. With 16,000 more employees, the nondurable goods sector saw the greatest increase in food production employment.

Average wages for workers in the industry
Workers in food manufacturing earn an average of $26,000 to $52,000 annually, while the highest-paid earn $52,000 annually. The range is higher for those with more years of experience, but the bottom 10 percent of earners earn less than $26,000 per year. Food Factory Workers are paid a high salary, but it is comparable to other positions in the manufacturing industry.
Average wages in this industry have increased over the last few years. While the manufacturing industry is important to our economy, it isn't an independent sector. The other sectors of the economy impact the lives of workers, making it important to understand how they relate to each other.
Locations with the most workers in the industry
In 2013, food manufacturing firms were concentrated in three New York State labor market regions: the Finger Lakes, the Southern Tier, and Western New York. These three regions together employed almost half of the total food manufacturing workforce. Food production in these regions was highly concentrated in these regions, with the highest average wages in the Hudson Valley, Southern Tier, and Western New York.
Food processing is a highly skilled industry. The lack of workers in some areas means that food manufacturing companies struggle to find workers with the proper skills. It's becoming more difficult to fill senior positions and to find workers for distribution trucks. According to a recent survey by career site CareersInFood.com, the number of open roles in food manufacturing has increased 12% in the past year, with a 37% increase in the past 24 months.
There are approximately 12,000 workers in this industry.
According to Bureau of Labor Statistics, February saw a 7.200 increase of workers in the food processing industry, an increase of over 1% compared to January. This is the third consecutive month of job gains for this industry, which is slowly recovering from several headwinds. The industry's unemployment has been affected by the COVID-19 virus pandemic, the labor shortage and the global recession. According to Bureau of Labor Statistics (Bolster of Labor Statistics), the industry employed 41,000 people in February.
From 2003 to 2013, the number of food manufacturing firms in New York State increased by 8%. Employment rose in four of the 10 labor-market regions, with the highest increases in the Southern Tier & Hudson Valley.
FAQ
How can efficiency in manufacturing be improved?
First, we need to identify which factors are most critical in affecting production times. We must then find ways that we can improve these factors. If you don’t know where to begin, consider which factors have the largest impact on production times. Once you've identified them all, find solutions to each one.
What are the differences between these four types?
Manufacturing refers the process of turning raw materials into useful products with machines and processes. Manufacturing can include many activities such as designing and building, testing, packaging shipping, selling, servicing, and other related activities.
What is the difference between Production Planning, Scheduling and Production Planning?
Production Planning (PP), also known as forecasting and identifying production capacities, is the process that determines what product needs to be produced at any particular time. This is done through forecasting demand and identifying production capacities.
Scheduling refers to the process of allocating specific dates to tasks in order that they can be completed within a specified timeframe.
What is the responsibility of a production planner?
Production planners ensure that all project aspects are completed on time, within budget and within the scope. They also ensure the quality of the product and service meets the client's requirements.
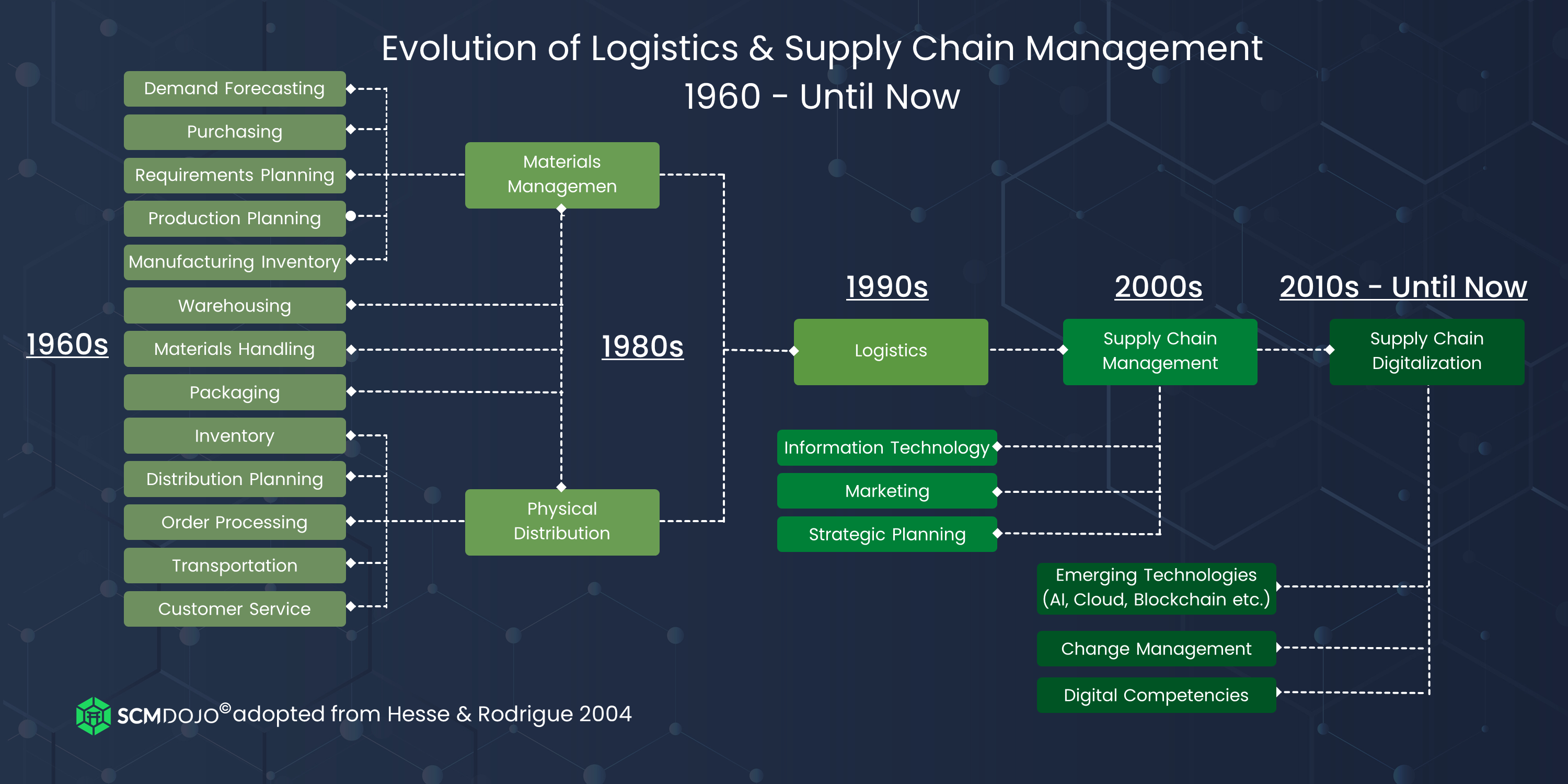
Are there any Manufacturing Processes that we should know before we can learn about Logistics?
No. It doesn't matter if you don't know anything about manufacturing before you learn about logistics. However, knowing about manufacturing processes will definitely give you a better understanding of how logistics works.
What skills are required to be a production manager?
To become a successful production planner, you need to be organized, flexible, and able to multitask. Also, you must be able and willing to communicate with clients and coworkers.
What is production planning?
Production planning is the process of creating a plan that covers all aspects of production. This includes scheduling, budgeting and crew, location, equipment, props, and more. This document is designed to make sure everything is ready for when you're ready to shoot. It should also provide information about how best to produce the best results while on set. This includes information on shooting times, locations, cast lists and crew details.
The first step is to outline what you want to film. You may have already chosen the location you want, or there are locations or sets you prefer. Once you've identified the locations and scenes you want to use, you can begin to plan what elements you need for each scene. One example is if you are unsure of the exact model you want but decide that you require a car. To narrow your options, you can search online for available models.
Once you have found the right car, you can start thinking about extras. Are you looking for people to sit in the front seats? Or perhaps you need someone walking around the back of the car? Maybe you'd like to change the interior from black to a white color. These questions will help guide you in determining the ideal look and feel for your car. Another thing you can do is think about what type of shots are desired. You will be filming close-ups and wide angles. Perhaps you want to show the engine or the steering wheel? This will allow you to determine the type of car you want.
Once you have made all the necessary decisions, you can start to create a schedule. A schedule will tell you when you need to start shooting and when you need to finish. The schedule will show you when to get there, what time to leave, and when to return home. This way, everyone knows what they need to do and when. If you need to hire extra staff, you can make sure you book them in advance. You don't want to hire someone who won't show up because he didn't know.
Also, consider how many days you will be filming your schedule. Some projects may only take a couple of days, while others could last for weeks. When creating your schedule, be aware of whether you need more shots per day. Multiple takes of the same location will lead to higher costs and take more time. If you aren't sure whether you need multiple shots, it is best to take fewer photos than you would like.
Budgeting is another important aspect of production planning. A realistic budget will help you work within your means. You can always lower the budget if you encounter unexpected problems. But, don't underestimate how much money you'll spend. If you underestimate the cost of something, you will have less money left after paying for other items.
Production planning can be a complex process. However, once you know how everything works together it will become easier to plan future projects.
Statistics
- You can multiply the result by 100 to get the total percent of monthly overhead. (investopedia.com)
- According to a Statista study, U.S. businesses spent $1.63 trillion on logistics in 2019, moving goods from origin to end user through various supply chain network segments. (netsuite.com)
- Many factories witnessed a 30% increase in output due to the shift to electric motors. (en.wikipedia.org)
- In 2021, an estimated 12.1 million Americans work in the manufacturing sector.6 (investopedia.com)
- It's estimated that 10.8% of the U.S. GDP in 2020 was contributed to manufacturing. (investopedia.com)
External Links
How To
How to Use Lean Manufacturing for the Production of Goods
Lean manufacturing is an approach to management that aims for efficiency and waste reduction. It was first developed in Japan in the 1970s/80s by Taiichi Ahno, who was awarded the Toyota Production System (TPS), award from KanjiToyoda, the founder of TPS. The first book published on lean manufacturing was titled "The Machine That Changed the World" written by Michael L. Watkins and published in 1990.
Lean manufacturing, often described as a set and practice of principles, is aimed at improving the quality, speed, cost, and efficiency of products, services, and other activities. It emphasizes the elimination of defects and waste throughout the value stream. Lean manufacturing is called just-in-time (JIT), zero defect, total productive maintenance (TPM), or 5S. Lean manufacturing seeks to eliminate non-value added activities, such as inspection, work, waiting, and rework.
Lean manufacturing not only improves product quality but also reduces costs. Companies can also achieve their goals faster by reducing employee turnover. Lean manufacturing is a great way to manage the entire value chain including customers, suppliers, distributors and retailers as well as employees. Lean manufacturing can be found in many industries. Toyota's philosophy is a great example of this. It has helped to create success in automobiles as well electronics, appliances and healthcare.
Lean manufacturing includes five basic principles:
-
Define Value - Determine the value that your business brings to society. Also, identify what sets you apart from your competitors.
-
Reduce waste - Stop any activity that isn't adding value to the supply chains.
-
Create Flow - Make sure work runs smoothly without interruptions.
-
Standardize and simplify - Make your processes as consistent as possible.
-
Building Relationships – Establish personal relationships with both external and internal stakeholders.
Lean manufacturing isn’t new, but it has seen a renewed interest since 2008 due to the global financial crisis. Many companies have adopted lean manufacturing methods to increase their marketability. Many economists believe lean manufacturing will play a major role in economic recovery.
With many benefits, lean manufacturing is becoming more common in the automotive industry. These include higher customer satisfaction levels, reduced inventory levels as well as lower operating costs.
The principles of lean manufacturing can be applied in almost any area of an organization. This is because it ensures efficiency and effectiveness in all stages of the value chain.
There are three types principally of lean manufacturing:
-
Just-in Time Manufacturing (JIT), also known as "pull system": This form of lean manufacturing is often referred to simply as "pull". JIT is a process in which components can be assembled at the point they are needed, instead of being made ahead of time. This strategy aims to decrease lead times, increase availability of parts and reduce inventory.
-
Zero Defects Manufacturing, (ZDM): ZDM is focused on ensuring that no defective products leave the manufacturing facility. You should repair any part that needs to be repaired during an assembly line. This is true even for finished products that only require minor repairs prior to shipping.
-
Continuous Improvement (CI): CI aims to improve the efficiency of operations by continuously identifying problems and making changes in order to eliminate or minimize waste. It involves continuous improvement of processes, people, and tools.