
Lean manufacturing, a management method that helps to reduce waste and increase efficiency, is what it stands for. It is inspired by the philosophies and practices of Henry Ford (previously president of Toyota Motor Corporation) and KiichiroToyoda (previous presidents). Manufacturing is not simply an assembly line. Lean manufacturing refers to it as a whole process. There are five key principles of lean: eliminate waste, streamline the process, create knowledge, optimize the whole, and use continuous improvement.
The first step in becoming lean is to identify what you are doing that is not adding value. This can be done using qualitative or quantitative techniques. Consider the price your customers pay to purchase your product. If the price of your product is higher than what you are offering, that's a sign you have a problem.
Kaizen events are a great way to assess the amount waste in a process. This is where everyone within the organization works together to solve problems incrementally. Kaizen events can either be used on their own or in conjunction other lean tools.
Value stream mapping is another way to identify production waste. VSM is a way for manufacturers to see the production steps and determine which are the most time-consuming.
Waste areas include inventory, waiting, overproduction, motion, and defects. These areas can be identified and improved by a lean team. They may be in the supply chain, in a production area, or throughout the whole process.
Once you have identified the problem, you can begin to implement strategies to eliminate it. These strategies include creating cross-functional teams, reducing your workload and training your employees to become multi-skilled. It depends on the business you have, but it may be worth considering technologies such as just in time or cell manufacturing. You can also utilize other lean tools such total productive maintenance or kanban administration.
The system can also include standardized containers, which allow workers and other personnel to easily know exact quantities without counting. The standardized containers also make it easier to detect if food or other materials are mixed in the products. Also, safety mats can be installed near machine areas that trigger a stoppage when a person steps on them.
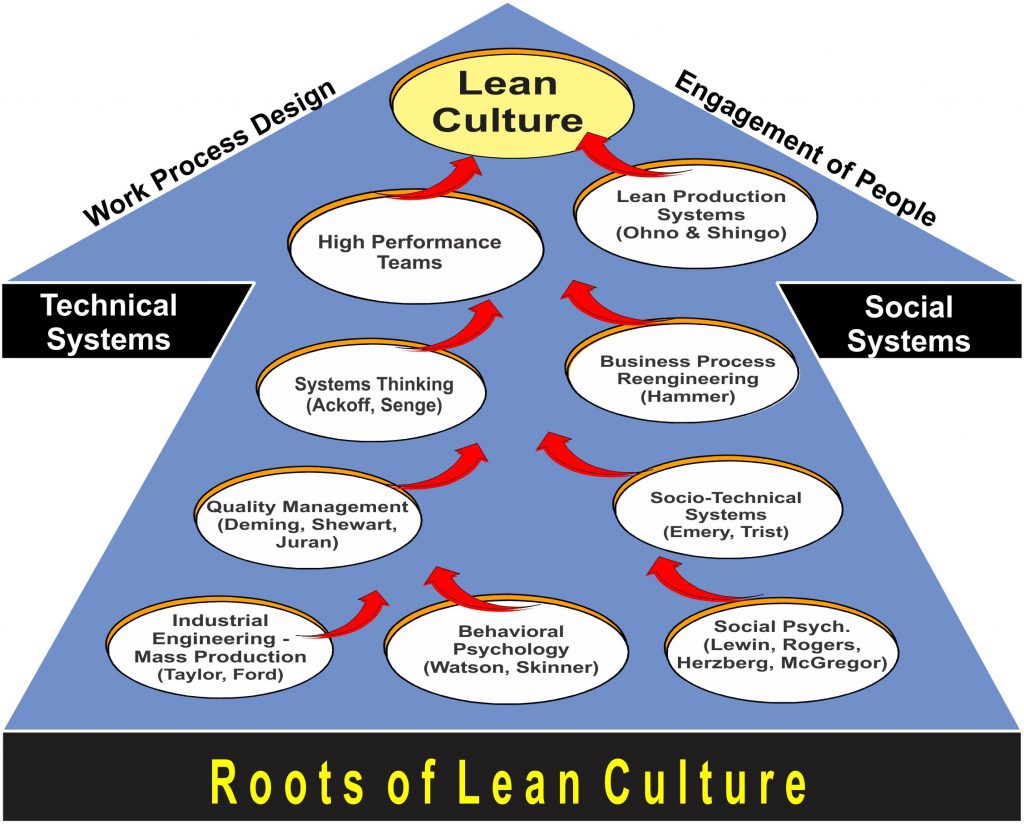
Strong organizational culture is crucial for any lean initiative. It should have communication skills, a clear understanding of the purpose of the initiative, and a long term focus. A sustainable system of improvement is essential to the success of your business.
When you're looking at a new machine, value stream mapping is a great tool. You can create an inventory that includes the future condition of your products, raw materials, and customer needs. This information allows you to more accurately predict when and how much equipment you will need. The same information can be used to create a scheduling system that will ensure you are able to fulfill orders on schedule.
By incorporating the five key principles of lean manufacturing, you can improve your organization's efficiency and help you achieve your goals. Visit various lean-manufacturing websites to learn more about the methods and resources that you have.
FAQ
What are the products of logistics?
Logistics refers to all activities that involve moving goods from A to B.
They include all aspects associated with transport including packaging, loading transporting, unloading storage, warehousing inventory management customer service, distribution returns and recycling.
Logisticians ensure that the product is delivered to the correct place, at the right time, and under safe conditions. They provide information on demand forecasts as well stock levels, production schedules and availability of raw material.
They keep track and monitor the transit of shipments, maintain quality standards, order replenishment and inventories, coordinate with suppliers, vendors, and provide support for sales and marketing.
What are the four types of manufacturing?
Manufacturing is the process that transforms raw materials into useful products. Manufacturing can include many activities such as designing and building, testing, packaging shipping, selling, servicing, and other related activities.
How can manufacturing avoid production bottlenecks
You can avoid bottlenecks in production by making sure that everything runs smoothly throughout the production cycle, from the moment you receive an order to the moment the product is shipped.
This includes planning for both capacity requirements and quality control measures.
The best way to do this is to use continuous improvement techniques such as Six Sigma.
Six Sigma is a management method that helps to improve quality and reduce waste.
It's all about eliminating variation and creating consistency in work.
What is the role and responsibility of a Production Planner?
Production planners ensure that all project aspects are completed on time, within budget and within the scope. They also ensure the quality of the product and service meets the client's requirements.
What kind of jobs are there in logistics?
There are different kinds of jobs available in logistics. Some examples are:
-
Warehouse workers - They load and unload trucks and pallets.
-
Transportation drivers - They drive trucks and trailers to deliver goods and carry out pick-ups.
-
Freight handlers: They sort and package freight in warehouses.
-
Inventory managers: They are responsible for the inventory and management of warehouses.
-
Sales reps are people who sell products to customers.
-
Logistics coordinators - They organize and plan logistics operations.
-
Purchasing agents: They are responsible for purchasing goods and services to support company operations.
-
Customer service representatives – They answer emails and phone calls from customers.
-
Shipping clerks: They process shipping requests and issue bills.
-
Order fillers – They fill orders based upon what was ordered and shipped.
-
Quality control inspectors – They inspect incoming and outgoing products to ensure that there are no defects.
-
Others - There is a variety of other jobs in logistics. These include transportation supervisors and cargo specialists.
Statistics
- According to a Statista study, U.S. businesses spent $1.63 trillion on logistics in 2019, moving goods from origin to end user through various supply chain network segments. (netsuite.com)
- Job #1 is delivering the ordered product according to specifications: color, size, brand, and quantity. (netsuite.com)
- In the United States, for example, manufacturing makes up 15% of the economic output. (twi-global.com)
- (2:04) MTO is a production technique wherein products are customized according to customer specifications, and production only starts after an order is received. (oracle.com)
- Many factories witnessed a 30% increase in output due to the shift to electric motors. (en.wikipedia.org)
External Links
How To
How to Use Just-In-Time Production
Just-in-time (JIT) is a method that is used to reduce costs and maximize efficiency in business processes. It is a process where you get the right amount of resources at the right moment when they are needed. This means you only pay what you use. Frederick Taylor was the first to coin this term. He developed it while working as a foreman during the early 1900s. He saw how overtime was paid to workers for work that was delayed. He realized that workers should have enough time to complete their jobs before they begin work. This would help increase productivity.
JIT is about planning ahead. You should have all the necessary resources ready to go so that you don’t waste money. Look at your entire project, from start to end. Make sure you have enough resources in place to deal with any unexpected problems. If you anticipate that there might be problems, you'll have enough people and equipment to fix them. This will prevent you from spending extra money on unnecessary things.
There are many JIT methods.
-
Demand-driven: This JIT is where you place regular orders for the parts/materials that are needed for your project. This will enable you to keep track of how much material is left after you use it. You'll also be able to estimate how long it will take to produce more.
-
Inventory-based: This is a type where you stock the materials required for your projects in advance. This allows one to predict how much they will sell.
-
Project-driven : This is a method where you make sure that enough money is set aside to pay the project's cost. Once you have an idea of how much material you will need, you can purchase the necessary materials.
-
Resource-based JIT: This is the most popular form of JIT. You assign certain resources based off demand. You will, for example, assign more staff to deal with large orders. If you don't have many orders, you'll assign fewer people to handle the workload.
-
Cost-based: This approach is very similar to resource-based. However, you don't just care about the number of people you have; you also need to consider how much each person will cost.
-
Price-based: This is a variant of cost-based. However, instead of focusing on the individual workers' costs, this looks at the total price of the company.
-
Material-based: This is quite similar to cost-based, but instead of looking at the total cost of the company, you're concerned with how much raw materials you spend on average.
-
Time-based JIT is another form of resource-based JIT. Instead of focusing solely on the amount each employee costs, focus on how long it takes for the project to be completed.
-
Quality-based JIT - This is another form of resource-based JIT. Instead of looking at the labor costs and time it takes to make a product, think about its quality.
-
Value-based JIT is the newest form of JIT. In this scenario, you're not concerned about how products perform or whether customers expect them to meet their expectations. Instead, you focus on the added value that you provide to your market.
-
Stock-based: This stock-based method focuses on the actual quantity of products being made at any given time. It's used when you want to maximize production while minimizing inventory.
-
Just-in-time (JIT) planning: This is a combination of JIT and supply chain management. It is the process that schedules the delivery of components within a short time of their order. It reduces lead times and improves throughput.