
DFSS (Design for Six Sigma) is a design methodology that uses a number of techniques to design a product, service, or process. It is used to reduce waste, improve product quality, and increase market shares. This is an effective methodology that can help you improve your products and services.
DFSS is a process where customer needs are considered throughout the design process. This allows you to design the right product or service for your customers. You can also guarantee that your product is high-quality when it's introduced to the market. DFSS can often be used to design a product/service completely from scratch. It is also used for designing products and/or services that can replace existing products or services.
The DFSS team will determine what the customer wants and needs in the initial phase. This may include interviewing customers, gathering information on existing processes and surveying them. To find the best match, the design team evaluates other products and designs. This phase includes the development and classification of functional requirements, as well as substitute concepts. Additional steps may be required depending on how complex the project is.

DFSS, a design methodology, is used to help companies design products or services efficiently and effectively. It helps to spot potential problems before they become major issues. It helps reduce waste and increases profitability. Its purpose is to identify process parameters that will make a product or services more effective.
There are several methods for implementing DFSS. DMADV is one of the most widely used methods. This involves a five step process. The process begins with the definition of the customer and their needs. Next, they create a design concept. This method is based on solid engineering principles and is used often to develop completely new products or services. The analysis and measurement phases are used to assess the product's performance.
The optimization phase is the second phase. This involves evaluating the product's performance at multiple levels. This step is very useful for developing new business procedures. This stage's goal is to reduce variation and ensure product stability over time.
The final stage involves the verification stage, which is often used to ensure that the product is stable. This stage also validates that the product is capable of performing over time. This process also includes validation testing. After the design is validated, validation testing is often completed.
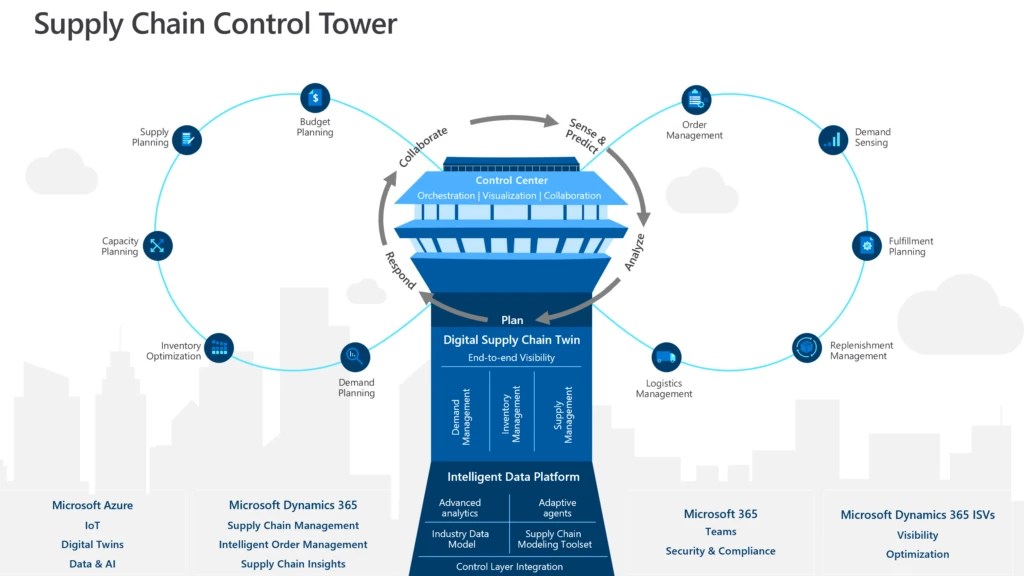
You need a process map to show all of the workflows involved in implementing DFSS. A detailed process map should contain information about resources, timeframes, milestones, as well as details about the budget. You must also be able pinpoint any external involvement required. To ensure the product meets customer needs, you may need to create a prototype. Implementing DFSS in an environment with clear rewards is a great way to achieve the project's goals.
FAQ
How can I learn about manufacturing?
The best way to learn about manufacturing is through hands-on experience. You can also read educational videos or take classes if this isn't possible.
What jobs are available in logistics?
There are many types of jobs in logistics. Some of them are:
-
Warehouse workers - They load trucks and pallets.
-
Transportation drivers: They drive trucks and trailers and deliver goods and make pick-ups.
-
Freight handlers, - They sort out and pack freight in warehouses.
-
Inventory managers – These people oversee inventory at warehouses.
-
Sales representatives - They sell products to customers.
-
Logistics coordinators - They plan and organize logistics operations.
-
Purchasing agents are those who purchase goods and services for the company.
-
Customer service representatives - They answer calls and emails from customers.
-
Shipping clerks: They process shipping requests and issue bills.
-
Order fillers - They fill orders based on what is ordered and shipped.
-
Quality control inspectors – They inspect incoming and outgoing products to ensure that there are no defects.
-
Others - There is a variety of other jobs in logistics. These include transportation supervisors and cargo specialists.
What is it like to manage a logistics company?
You need to have a lot of knowledge and skills to manage a successful logistic business. Good communication skills are essential to effectively communicate with your suppliers and clients. You should be able analyse data and draw inferences. You must be able manage stress and pressure under pressure. In order to innovate and create new ways to improve efficiency, creativity is essential. To motivate and guide your team towards reaching organizational goals, you must have strong leadership skills.
You should also be organized and efficient to meet tight deadlines.
Why is logistics so important in manufacturing?
Logistics are an integral part any business. Logistics can help you achieve amazing results by helping to manage product flow from raw materials to finished products.
Logistics also play a major role in reducing costs and increasing efficiency.
What do we need to know about Manufacturing Processes in order to learn more about Logistics?
No. No. Knowing about manufacturing processes will help you understand how logistics works.
Statistics
- In the United States, for example, manufacturing makes up 15% of the economic output. (twi-global.com)
- You can multiply the result by 100 to get the total percent of monthly overhead. (investopedia.com)
- Many factories witnessed a 30% increase in output due to the shift to electric motors. (en.wikipedia.org)
- It's estimated that 10.8% of the U.S. GDP in 2020 was contributed to manufacturing. (investopedia.com)
- Job #1 is delivering the ordered product according to specifications: color, size, brand, and quantity. (netsuite.com)
External Links
How To
How to use the Just-In Time Method in Production
Just-in time (JIT), is a process that reduces costs and increases efficiency in business operations. It allows you to get the right amount resources at the right time. This means that your only pay for the resources you actually use. Frederick Taylor developed the concept while working as foreman in early 1900s. Taylor observed that overtime was paid to workers if they were late in working. He concluded that if workers were given enough time before they start work, productivity would increase.
JIT is an acronym that means you need to plan ahead so you don’t waste your money. The entire project should be looked at from start to finish. You need to ensure you have enough resources to tackle any issues that might arise. You'll be prepared to handle any potential problems if you know in advance. You won't have to pay more for unnecessary items.
There are many JIT methods.
-
Demand-driven JIT: This is a JIT that allows you to regularly order the parts/materials necessary for your project. This will allow you to track how much material you have left over after using it. This will allow you to calculate how long it will take to make more.
-
Inventory-based: This type allows you to stock the materials needed for your projects ahead of time. This allows you predict the amount you can expect to sell.
-
Project-driven: This is an approach where you set aside enough funds to cover the cost of your project. Once you have an idea of how much material you will need, you can purchase the necessary materials.
-
Resource-based JIT: This is the most popular form of JIT. Here, you allocate certain resources based on demand. For example, if there is a lot of work coming in, you will have more people assigned to them. You'll have fewer orders if you have fewer.
-
Cost-based: This is a similar approach to resource-based but you are not only concerned with how many people you have, but also how much each one costs.
-
Price-based pricing: This is similar in concept to cost-based but instead you look at how much each worker costs, it looks at the overall company's price.
-
Material-based: This approach is similar to cost-based. However, instead of looking at the total cost for the company, you look at how much you spend on average on raw materials.
-
Time-based: Another variation of resource-based JIT. Instead of worrying about how much each worker costs, you can focus on how long the project takes.
-
Quality-based: This is yet another variation of resource-based JIT. Instead of worrying about the costs of each employee or how long it takes for something to be made, you should think about how quality your product is.
-
Value-based JIT: One of the most recent forms of JIT. This is where you don't care about how the products perform or whether they meet customers' expectations. Instead, you're focused on how much value you add to the market.
-
Stock-based: This is an inventory-based method that focuses on the actual number of items being produced at any given time. It's useful when you want maximum production and minimal inventory.
-
Just-intime planning (JIT), is a combination JIT/sales chain management. It is the process that schedules the delivery of components within a short time of their order. It is essential because it reduces lead-times and increases throughput.