
Manufacturing engineering is sometimes referred to simply as engineering production. This type shares many ideas and concepts with other engineering areas. Engineers who specialize in this area can find their own niche within an industry and become integral to the success of a company. These engineers are capable of ensuring that a product meets high quality standards.
Job duties
Production engineers coordinate and analyze the production process from design to completion. This position requires attention to detail, and commitment to safety in the workplace. Production engineers make sure that their company adheres to high quality standards. They also assess existing production activities to determine ways to improve.
A production engineer helps a company produce products quickly and affordably, and they also play a key role in implementing automation. Their work may include analyzing current production processes, as well as focusing their attention on one aspect of the production process. They may also help adjust the software running plant equipment and train production workers.
You must have excellent communication skills to do the job. Engineers must be able explain complicated engineering concepts clearly. This is because engineering can involve complex mathematics and calculations. To determine the cost of finished products or to solve manufacturing problems, a production engineer might use equations.
Education necessary
First, earn a bachelor’s degree in industrial or manufacturing engineering to get a job as a production engineer. Employers may prefer to have a master's degree especially for positions in research-oriented manufacturing. It is helpful to have proficiency in one or several specialized areas.
Industrial engineers apply their creativity and analytical skills in order to increase the efficiency of production processes. They are interested in reducing waste and developing new ways to make use of equipment and workers. A good communication skill is essential as they need to be able explain complicated processes to non-technical people. A good communication skill includes the ability to listen attentively and fully comprehend the opinions and views of others.
Manufacturing engineers learn hands-on skills during the degree program. They will also learn about safety regulations. The National Society of Professional Engineers will require them to obtain a Professional Engineer License. This license proves to employers and clients you have the right credentials. Renewing your license should be done according to the state's requirements.
Salary
The salary of production engineers varies depending on their location and company. Although they are primarily employed in offices, production engineers may travel to work on site to inspect equipment and improve processes. Some production engineers work independently, while others work in larger companies. In addition to their salary, production engineers are expected to complete their work in a timely manner.
Production engineers collaborate with other professionals to ensure that the product is safe and quality. They will also work closely with designers to ensure the most efficient production processes. In some cases, they may be responsible for maintaining safety standards in the factory and training workers about proper safety procedures. Although this job description is not exhaustive, it provides an overview of the duties and responsibilities for a production engineer.
Production engineers' salaries depend on their level of experience. Entry-level production engineers earn approximately Rs2.5 lakhs annually. Mid-level engineers could earn Rs3.8 Lakhs. For experienced production engineers, the annual salary can rise to Rs3.8 lakhs.
FAQ
How can manufacturing efficiency improved?
First, identify the factors that affect production time. Then we need to find ways to improve these factors. If you don’t know where to begin, consider which factors have the largest impact on production times. Once you have identified them, it is time to identify solutions.
What does warehouse refer to?
A warehouse is a place where goods are stored until they are sold. It can be indoors or out. In some cases it could be both indoors and outdoors.
What is it like to manage a logistics company?
To be a successful businessman in logistics, you will need many skills and knowledge. To communicate effectively with clients and suppliers, you must be able to communicate well. It is important to be able to analyse data and draw conclusions. You must be able to work well under pressure and handle stressful situations. To increase efficiency and creativity, you need to be creative. You need to have strong leadership qualities to motivate team members and direct them towards achieving organizational goals.
It is also important to be efficient and well organized in order meet deadlines.
Statistics
- Many factories witnessed a 30% increase in output due to the shift to electric motors. (en.wikipedia.org)
- (2:04) MTO is a production technique wherein products are customized according to customer specifications, and production only starts after an order is received. (oracle.com)
- In the United States, for example, manufacturing makes up 15% of the economic output. (twi-global.com)
- It's estimated that 10.8% of the U.S. GDP in 2020 was contributed to manufacturing. (investopedia.com)
- [54][55] These are the top 50 countries by the total value of manufacturing output in US dollars for its noted year according to World Bank.[56] (en.wikipedia.org)
External Links
How To
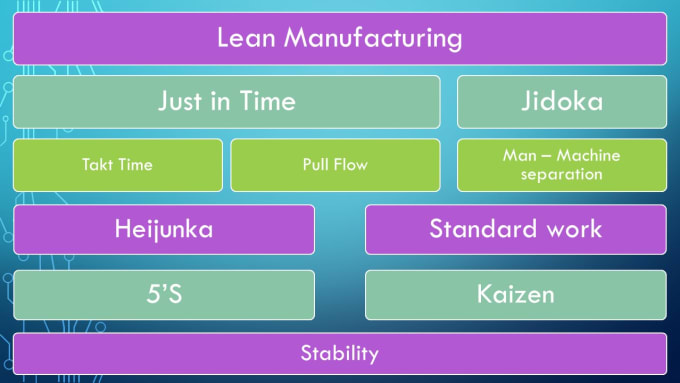
How to Use Lean Manufacturing for the Production of Goods
Lean manufacturing is a management style that aims to increase efficiency and reduce waste through continuous improvement. It was created in Japan by Taiichi Ohno during the 1970s and 80s. He received the Toyota Production System award (TPS), from Kanji Toyoda, founder of TPS. Michael L. Watkins published the "The Machine That Changed the World", the first book about lean manufacturing. It was published in 1990.
Lean manufacturing refers to a set of principles that improve the quality, speed and costs of products and services. It emphasizes reducing defects and eliminating waste throughout the value chain. Just-in-time (JIT), zero defect (TPM), and 5S are all examples of lean manufacturing. Lean manufacturing emphasizes reducing non-value-added activities like inspection, rework and waiting.
Lean manufacturing can help companies improve their product quality and reduce costs. Additionally, it helps them achieve their goals more quickly and reduces employee turnover. Lean manufacturing is a great way to manage the entire value chain including customers, suppliers, distributors and retailers as well as employees. Lean manufacturing is widely practiced in many industries around the world. For example, Toyota's philosophy underpins its success in automobiles, electronics, appliances, healthcare, chemical engineering, aerospace, paper, food, etc.
Five principles are the basis of lean manufacturing:
-
Define Value - Identify the value your business adds to society and what makes you different from competitors.
-
Reduce Waste - Eliminate any activity that doesn't add value along the supply chain.
-
Create Flow. Ensure that your work is uninterrupted and flows seamlessly.
-
Standardize & Simplify - Make processes as consistent and repeatable as possible.
-
Develop Relationships: Establish personal relationships both with internal and external stakeholders.
Although lean manufacturing has always been around, it is gaining popularity in recent years because of a renewed interest for the economy after 2008's global financial crisis. Many businesses have adopted lean manufacturing techniques to help them become more competitive. Economists think that lean manufacturing is a crucial factor in economic recovery.
Lean manufacturing has many benefits in the automotive sector. These include higher customer satisfaction levels, reduced inventory levels as well as lower operating costs.
Any aspect of an enterprise can benefit from Lean manufacturing. Because it makes sure that all value chains are efficient and effectively managed, Lean Manufacturing is particularly helpful for organizations.
There are three types principally of lean manufacturing:
-
Just-in Time Manufacturing, (JIT): This kind of lean manufacturing is also commonly known as "pull-systems." JIT means that components are assembled at the time of use and not manufactured in advance. This method reduces lead times, increases availability, and decreases inventory.
-
Zero Defects Manufacturing (ZDM): ZDM focuses on ensuring that no defective units leave the manufacturing facility. It is better to repair a part than have it removed from the production line if it needs to be fixed. This is true even for finished products that only require minor repairs prior to shipping.
-
Continuous Improvement (CI), also known as Continuous Improvement, aims at improving the efficiency of operations through continuous identification and improvement to minimize or eliminate waste. Continuous improvement refers to continuous improvement of processes as well people and tools.